Executive Office for United States Attorneys
Executive Office for United States Attorneys Organizational Chart
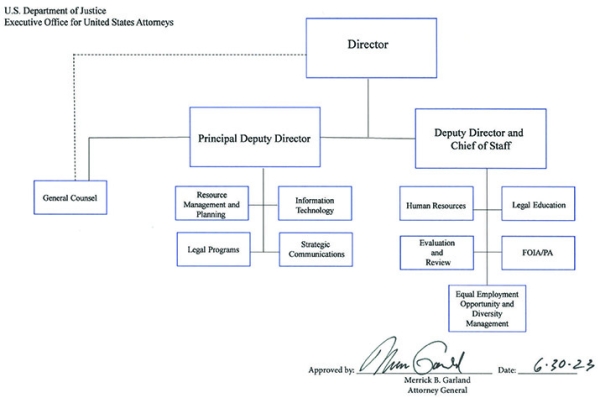
- Director
- General Counsel
- Principal Deputy Director
- Resource Management and Planning
- Information Technology
- Legal Programs
- Strategic Communications
- Deputy Director
- Human Resources
- Legal Education
- Evaluation and Review
- FOIA/PA
- Equal Employment Opportunity and Diversity Management
Approved by Merrick B. Garland, Attorney General June 30, 2023
History
The Executive Office for United States Attorneys (EOUSA) was created on April 6, 1953, by Attorney General Order No. 8-53, to meet a need for closer liaison between the Department of Justice in Washington, D.C., and the United States Attorneys. The Executive Office is under the supervision of a Director, who is appointed by the Attorney General and reports to the Deputy Attorney General.
Mission
The mission of EOUSA is to provide general executive assistance and supervision to the 94 Offices of the United States Attorneys and to coordinate and direct the relationship between the United States Attorneys and the organizational components of the Department of Justice and other federal agencies in Washington, D.C.
Major Functions
The major functions of EOUSA are to:
- Provide advice and support to the Attorney General and Deputy Attorney General regarding United States Attorney appointments.
- Manage the United States Attorneys’ appropriation, including direct and indirect budget authority and personnel resources. Provide budget and fiscal assistance and guidance to the United States Attorneys’ offices.
- Analyze statistical data and provide reports and recommendations related to the work and resources of the United States Attorneys’ offices.
- Provide overall administrative management oversight and support to the United States Attorneys’ offices in the areas of facilities management (including acquisition of real property and office space, construction, renovation, repair, and relocation), and support service programs (including personal property management, simplified acquisition, motor vehicle support, records disposition, and forms management).
- Formulate, implement, and administer bureau-level human resource management policies and programs for the 94 United States Attorneys’ offices, including programs affecting Assistant United States Attorneys appointed under Title 28 and compensated under a separate pay system, as well as support staff appointed under Title 5. Provide technical oversight of the United States Attorneys’ offices with delegated personnel authorities and provide operating personnel and pre-employment security services to the other United States Attorneys’ offices.
- Provide management oversight and support to the United States Attorneys’ offices in the planning, development, implementation, and administration of comprehensive security programs encompassing all aspects of physical, communication, information, personnel, and computer security.
- Develop, acquire, and manage a full range of integrated information technology systems and software applications in the United States Attorneys’ offices. Provide technical, administrative, design, and maintenance support in the areas of voice, data, and video telecommunications to provide efficient communications.
- Evaluate the performance of the United States Attorneys’ offices, making appropriate reports and inspections, taking corrective actions, and providing management assistance where needed.
- Provide advice, support, and guidance regarding the management and operation of legal programs and initiatives in the United States Attorneys’ offices, including debt collection, criminal prosecution, affirmative civil enforcement, defensive civil litigation, asset forfeiture, and victim assistance.
- Provide legal advice and assistance to the United States Attorneys and other managers in EOUSA and the United States Attorneys’ offices on disciplinary or performance actions, grievances, standards of ethical conduct, recusals, and fiscal law issues, and represent the Department in administrative litigation arising out of EOUSA and the United States Attorneys’ offices.
- Provide centralized leadership, coordination, and processing of all equal employment efforts throughout the United States Attorneys’ offices – administering both the Affirmative Employment and Complaints Processing Programs.
- Respond to Freedom of Information Act and Privacy Act (FOIA/PA) requests for all the United States Attorneys’ offices and EOUSA; handle litigation arising from these matters; and provide FOIA/PA advice and training to the United States Attorneys’ staffs.
- Provide advice, support, and guidance to the United States Attorneys’ offices on congressional relations and pending legislation pertinent to their work. Prepare testimony and background for congressional oversight and appropriations hearings.
- Provide advice, support, and guidance regarding public affairs, website and social media management, and strategic communications.
- Publish and maintain the Justice Manual and Department of Justice Journal of Federal Law and Practice.
- Oversee the Office of Legal Education, which develops and conducts training for all Department of Justice attorney and non-attorney legal personnel, and United States Attorney and EOUSA administrative personnel.
- Assist the Attorney General’s Advisory Committee of United States Attorneys and its subcommittees and working groups by providing staff and funds as needed to carry out the Committee’s responsibilities.
United States Attorneys
The United States Attorneys serve as the nation’s principal litigators under the direction of the Attorney General. United States Attorneys are Presidentially-appointed, Senate-confirmed and they serve at the pleasure of the President of the United States. There are 93 United States Attorneys stationed throughout the United States and its territories; one U.S. Attorney is assigned to each of the 94 judicial districts, with the exception of Guam and the Northern Mariana Islands, where a single United States Attorney serves in both districts. Each United States Attorney is the chief federal law enforcement officer of the United States within their jurisdiction.
United States Attorneys oversee most of the trial work in which the United States is a party. United States Attorneys have three statutory responsibilities under Title 28, Section 547 of the United States Code:
- The prosecution of criminal cases brought by the Federal Government;
- The prosecution and defense of civil cases in which the United States is a party; and
- The collection of debts owed to the Federal Government that are administratively uncollectible.
Although the distribution of caseload varies between districts, each handles every category of cases, including a mixture of simple and complex litigation. Each United States Attorney exercises wide discretion in the use of his or her resources to further the priorities of the local jurisdictions and the needs of their communities.