

U.S. Department of Justice
National Drug Intelligence Center
New Mexico HIDTA Drug Market Analysis 2010
May 2010
 To
Contents
To Previous Page
To Next Page
To Publications
Page
To Home Page
To
Contents
To Previous Page
To Next Page
To Publications
Page
To Home Page


U.S. Department of Justice
National Drug Intelligence Center
New Mexico HIDTA Drug Market Analysis 2010
May 2010
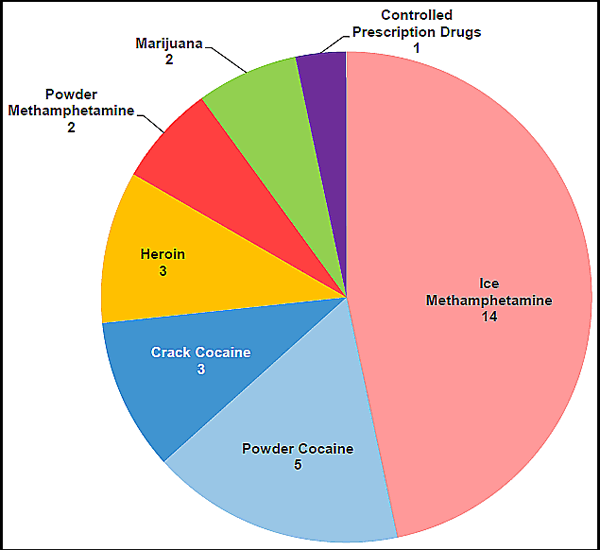
The distribution and abuse of ice methamphetamine are the greatest drug threats to the New Mexico HIDTA region. According to National Drug Intelligence Center (NDIC) National Drug Threat Survey (NDTS) 2010 data, 14 of the 30 responding law enforcement agencies in the New Mexico HIDTA identify ice methamphetamine as the greatest drug threat in their jurisdictions. (See Figure 3.) Most methamphetamine available in the New Mexico HIDTA region is produced in Mexico. Local methamphetamine production takes place in the region but has been decreasing.
Figure
3. Greatest Drug Threat in the New Mexico HIDTA Region as Reported by
State and Local Law Enforcement Agencies, by Number of Respondentsa
d-link
Source: National Drug Threat Survey 2010.
The distribution and abuse of powder and crack cocaine and heroin also pose significant law enforcement challenges. Powder cocaine is the greatest threat in Bernalillo and Dona Ana Counties, while crack cocaine is the greatest threat in the southern New Mexico counties of Lea, Luna, and Otero. (See Appendix A.) Most heroin is distributed and abused in the northern New Mexico counties of Bernalillo, Rio Arriba, Sandoval, and Valencia. Heroin abuse in these counties is often multigenerational, making it difficult for law enforcement and treatment providers to stem the abuse.
The smuggling and transshipment of marijuana are a threat to the New Mexico HIDTA, particularly in Hidalgo (Boot Heel region) and Luna Counties in southern New Mexico. Law enforcement officers in the New Mexico HIDTA seized more marijuana than any other illicit drug each year from 2007 through 2009. Small amounts of marijuana are also produced in the New Mexico HIDTA at both outdoor and indoor grows.
Availability and abuse of MDMA increased in the New Mexico HIDTA region in 2009, primarily in southern New Mexico, where law enforcement reporting indicates that young adults are abusing MDMA in the local area rather than risking participation in the night life of Juárez, where border violence is prevalent. Law enforcement reporting indicates that most of the available MDMA is produced in Mexico and transported from the El Paso area to the HIDTA region for distribution. Seizures range from small, user quantities to multihundred-tablet amounts. For example, in November 2009, two female New Mexico residents were apprehended by officers at the El Paso POE while attempting to smuggle five MDMA tablets and an unidentified amount of ketamine. Task Force officers in southern New Mexico report 300- to 500-tablet seizures of the drug.
a. NDTS data for 2010 cited in this report are as of March 3, 2010. NDTS data cited are raw, unweighted responses from federal, state, and local law enforcement agencies solicited through either NDIC or the Office of National Drug Control Policy (ONDCP) HIDTA program. Data cited may include responses from agencies that are part of the NDTS 2010 national sample or agencies that are part of HIDTA solicitation lists.
UNCLASSIFIED
End of page.